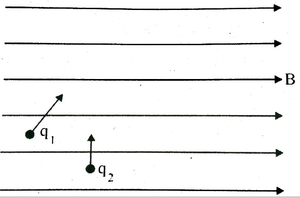
| Two charged particles q1 and q2 are moving through a uniform magnetic field (B) as shown in figure (a) What is the shape of path of q1 and q2 (b) Derive an expression for cyclotron frequency with the help of a neat diagram. |
 |
| Previous Year Questions of March Examinations from 2010 to 2020 |
| Chapter Name: MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM |
|
Ampere’s circuital theorem is generally used to determine the magnetic field produced by a current carrying element. a) State Ampere’s circuital theorem. b) Obtain an expression for the magnetic field produced by an infinitely long straight conductor using Ampere’s circuital theorem. c) A long straight conductor carries 35 ampere. Find the magnetic field produced due to this conductor at a point 20 cm away from the centre of the wire. |
|
A galvanometer is used to detect current in a circuit. a) State the working principle of a moving coil galvanometer. b) How will you convert a galvanometer into (i) an ammeter (ii) a voltmeter? c) A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 ohms. It shows a full scale deflection for a current of 3 mA. How will you convert this into a voltmeter of range 0-18 V? |
|
You are sitting in a room in which a uniform magnetic field B exists. At the centre of the room a charged particle is suddenly projected horizontally and it starts circular motion in the horizontal plane. a) What should be the direction of the magnetic field for this to happen? b) Will there be a change in kinetic energy of the particle due to this circular motion? Why? c) A cyclotron uses a magnetic field and an electric field to increase the energy of a charged particle. Describe its construction and working. |
|
Oersted found that moving charges or currents produce a magnetic field in the surrounding space. a) An electric current is flowing due to south along a power line. What is the direction of magnetic field (i) above it and (ii) below it? b) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a cyclotron. State the underlying principle of its working. c) A cyclotron’s oscillator frequency is 10 MHz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons? e = 1.6×10 -19 C, mass of proton mp =1.67×10 -27 kg |
|
Force acting on a charged particle when it moves in a combined electric and magnetic field is known as Lorentz force a) A charged particle is released from rest in a region of steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields; which are parallel to each other. What will be the nature of the path followed by the charged particle? Explain your answer b) a rectangular loop carrying a steady current is placed in a uniform magnetic field. Obtain the expression for the torque acting on the loop |
|
The relation between magnetic field and current is given by Biot-Savart law a) Illustrate Biot-Savart law with necessary figure b) Compare Biot-Savart law with Coulomb’s law for electrostatic field c) Give an expression for magnetic field on the axis of a circular current loop. (Expression only) d) What is the value of B at the centre of the loop? |
|
Transformers either increase or decrease AC voltage (A) State the principle of a transformer (B) Explain with a labelled diagram the working of a transformer (C) Explain briefly any three energy losses in a transformer |
|
A current carrying wire produces a magnetic field in its surrounding space (A) The SI unit of magnetic field density is (a) henry (b) tesla (c) Am 2 (d) A-m (B) With the help of a diagram, derive an expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a circular current loop (C) Consider a tightly wound 100 turn coil of radius 10cm, carrying a current of 1A. What is the magnitude of magnetic field at the centre of the coil? |
|
A moving charge can produce a magnetic field (a) How does a current loop behaves like a magnetic dipole? (b) Draw the magnetic field lines for a current loop to support your answer (c) (i) What is a cyclotron? (ii) Write down the expression for cyclotron frequency |
|
(a) An electric charge q is moving with a velocity v in the direction of a magnetic field B. The magnetic force acting on the charge is (i) qvB (ii)zero (iii) q/B (iv) v/qB (b) Starting from Biot-Savart law, obtain an expression for the magnetic field at an axial point of a circular coil carrying current |
|
(a) An ammeter is a curent measuring device which is always connected in ...... in an electric circuit (b) Describe a cyclotron and obtain an expression for cyclotron frequency |
| Two charged particles q1 and q2 are moving through a uniform magnetic field (B) as shown in figure (a) What is the shape of path of q1 and q2 (b) Derive an expression for cyclotron frequency with the help of a neat diagram. |
 |
| A charged particle enters a uniform magnetic field at an angle of 40°. It"s path becomes ...... |
|
Cyclotron is a device used to accelerate charged particles. (a) With a suitable diagram briefly explain the working of a cyclotron and obtain an expression for cyclotron frequency. (b) A cyclotron oscillator frequency is 10 M Hz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons ? |
|
The path of a charged particle entering parallel to uniform magnetic field will be (a) circular (b) helical (c) straight line (d) None of these |
|
Ampere"s theorem helps to find the magnetic field in a region around a current carrying conductor. (a) Write the expression of Ampere"s theorem. (b) Draw a graph showing the variation of intensity of magnetic field with the distance from the axis of a current carrying conductor. |
|
A rectangular loop of area A and carrying a steady current I is placed in a uniform magnetic field. (a) Derive the expression of torque, τ = m x B , acting on the loop. (b) Increasing the current sensitivity may not necessarily increase the voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer. Justify. |