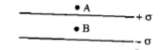
| a) Name the physical quantity which has its unit joule.coulomb -1 . Is it a vector or a scalar? b) Two plane sheets of charge densities +σ and -σ are kept in air as shown in figure. What are the electric field intensities at points A and B? |
 |
| Previous Year Questions of March Examinations from 2010 to 2020 |
| Chapter Name: ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS |
|
A body of mass m is charged negatively. State whether the following statements are true or false. a) During charging, there is change in mass of body. b) The body can be charged to 2.5e where ‘e’ is the charge of an electron. c) While charging the body by induction new charges are created in it. d) The force between two charged objects is less when there is a medium between them (than in vacuum). |
| a) Name the physical quantity which has its unit joule.coulomb -1 . Is it a vector or a scalar? b) Two plane sheets of charge densities +σ and -σ are kept in air as shown in figure. What are the electric field intensities at points A and B? |
 |
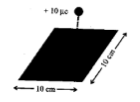
| The idea of ‘Electric field lines’ is useful in pictorially mapping the electric field around charges. a) Give any two properties of electric lines of force. b) State Gauss’s electrostatics. Theorem, in Electrostatic. c) Using the theorem, derive an expression for electric field due to a uniformly charged spherical shell i) at point outside the shell ii) at a point inside the shell d) A point charge of +10 μc is at a distance of 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm as shown in figure. What is the electric flux through the square? |
 |
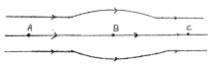
| The region around a charge where its effect can be felt is called the electric field. a) The electric field lines corresponding to an electric field is shown The figure suggests that i) EA > EB >EC ii) EA = EB = EC iii) EA < EB < EC iv) EA = EB > EC v) EA = EC > EB |
 |
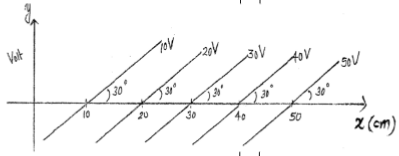
| Some equipotential surfaces are shown in the figure. What can you say about the magnitude and direction of the electric field? |
 |
|
Gauss s law can be used to determine the electric field due to a charge distribution a) Below are some statements about Gauss’s law. Say whether they are true or false: i) Gauss s law is valid only for symmetrical charge distribution ii) The electric field calculated by Gauss’s law is the field due to charges inside the Gaussian surface b) Apply Gauss s law to find the electric field due to an infinitely long plane sheet of charge c) “There can be no net charge in a region in which the electric field is uniform at all points”. Do you agree with this statement? Justify your answer |
|
A) All free charges are integral multiple of a basic unit charge e. Then quantization
rule of electric charge implies a) Q = e b) Q = ne c) Q = 1 / e d) Q = e B) Match the following quantities in Column A with their units in Column B:
|
| Electric field is an important way of characterising the electrical environment of a system of charges. Two point charges q1 and q2 of magnitude +10-8 C and -10-8 C respectively are placed 0.1 m apart. Calculate the electric fields at points A, B and C shown in the figure |
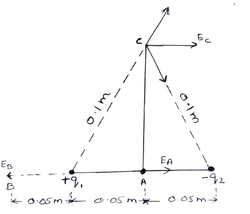 |
|
Electric field lines are a pictorial representation of electric field around charges (A) State Gauss’s law in electrostatics (B) Using this law derive an expression for the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell at a point (i) Outside the shell (ii) Inside the shell (C) Suppose you are in a cave deep within the earth. Are you safe from thunder and lightning? Why? |
|
(a) State Gauss’s law for magnetism? (b) How this differs from Gauss’ law for electrostatics? (c) Why is the difference in the two cases? |
|
(a) How much greater is one micro coulomb compared to an electronic charge? (i) 1013 times (ii) 1011 times (iii) 1010 times (iv) 106 times (b) A point charge of 2 μc is placed at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface of side 0.5 cm. What is the next flux through the surface? (Given ε0 =8.85 x 10 -12C2 /N/m2 ) |
|
a) How many electrons constitute an electric charge of -16 μC? (i) 1013 (ii) 1014 (iii) 1015 (iv) 1012 (b) An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges +q and -q separated by a distance r. Write an expression for its dipole moment. (c) When an electric dipole is subjected to a uniform electric field, what will happen? |
| Two equal and opposite charges placed in air as shown in figure: (a) Redraw the figure and show the direction of dipole moment (P), direction of resultant electric field (E) at P. (b) Write an equation to find out the electric field at P. |
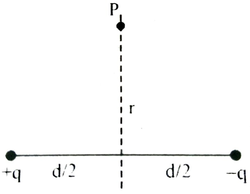 |
| Two spheres enclose charges as shown in figure: (a) Derive an expression for electric field intensity at any point on the surface S2 (b) What is the ratio of electric flux through S1 and S2 ? |
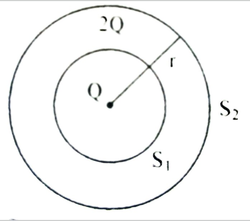 |
|
(a) The ratio of electric field on the equatorial point and at the axial point at equal distances from the centre of a short electric dipole is ......................... (b) A closed surface encloses an electric dipole. What is the electric flux through the surface ? |
|
A spherical shell of radius R is uniformly charged with charge +q. By Gauss"s theorem, find the electric field intensity at a point p. (a) Outside the spherical shell and (b) Inside the spherical shell. |
| A permanent electric dipole of dipole moment p is placed in a uniform external electric field E, as shown in Figure. (a) Redraw the figure and show the magnitude and direction of force acting on the charges. (b) Write an expression of the torque acting on this dipole in vector form. |
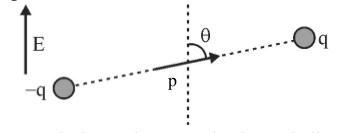 |
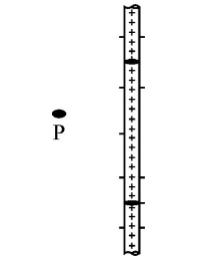
| An infinitely long thin straight wire with uniform linear charge density is shown in figure. (a) Draw a Gaussian surface in order to calculate the electric field at P and mark direction of electric field at this point. (b) Derive an expression to calculate electric field at this point P. |
 |